Eine Welt ohne Kupfer ist schwer vorstellbar. Wir verlassen uns auf Kupfer beim Strom, der Beleuchtung, der Heizung, der Kommunikation, der Wasserversorgung und dem Transport. Kupfer macht unsere Häuser, Schulen und Unternehmen effizient, gemütlich und dekorativ und es hält viele Jahre. Kupfer verfügt über eine hervorragende Eigenschaftskombination. Es ist sowohl ein guter elektrischer und thermischer Leiter als auch dehnbar und kann bakterielles Wachstum verhindern.
Kupfer eignet sich sehr gut fürs Recyceln, weil es unendlich viele Male wieder eingeschmolzen werden kann ohne dabei seine Eigenschaften zu verlieren. In Zukunft wird es sich sogar lohnen, die wenigen Gramm Kupfer in eurem Handy wiederzugewinnen! [1]
Where do the raw materials and components come from?

Copper is contained with 0.01 percent in the earth’s crust. Rarely, copper is considered as pure metal. There are now a few hundred copper minerals called ores. The most important copper ores are: chalcopyrite, malachite and boronite. More than 50% of the world’s copper is derived from these minerals, which is the most productive source. [1]
How is copper produced?
Metals are found as ores buried in the earth’s crust. How do we get to the final metal? There are three main phases: mining, extraction and cleaning.
- Reduction:
There are two methods for breaking down ore:
Underground construction: Construction of a vertical shaft in the ground to a corresponding depth and propulsion of horizontal tunnel sections into the ore.
Opencast mining: 90% of the ore is extracted using this method. Near-surface ore deposits can be degraded after removal of the surface layers.
- Extraction:
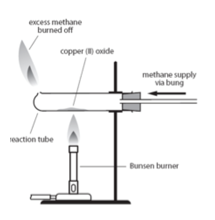
The ore must be chemically converted into metal. This process is called reduction.
From: Copper oxide (Cu2O) + iron (Fe) REDUCTION to: copper (Cu) + iron oxide (Fe2O3)
- Cleaning
Many metals are unclean when they are extracted from their ores. Contaminations must be removed. Copper is purified by electrolysis. In this process, impurities on the soil and copper are trapped in so-called electrolytic cells. The copper obtained by this process is 99.99% pure copper. [1]
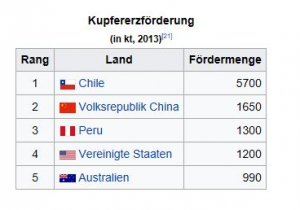
Where is copper produced?
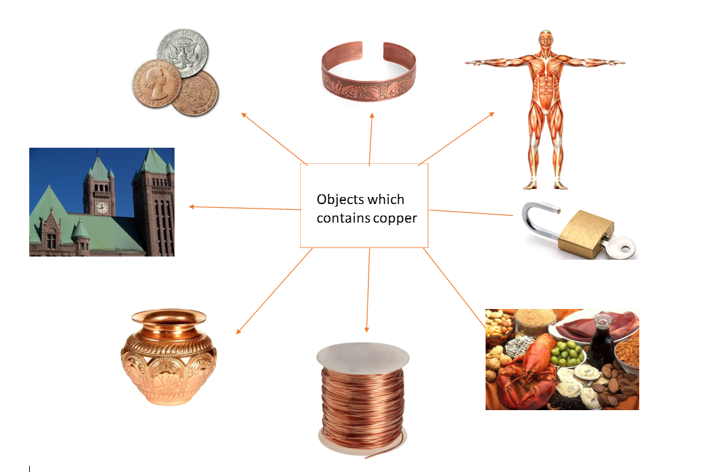
In which products can we find copper?
How it’s recycled?
The process of copper recycling involves several main steps:
The first is to visually inspect the copper scrap and separate it into two main groups; clean unalloyed scrap and scrap that is alloyed and includes oxidised or coated pieces.
The clean scrap is then melted down, analysed to check its purity level while molten, and then deoxidised and cast into moulds such as cakes or ingots. The contaminated scrap is also melted down and cast into moulds. It is then refined using a process known as electrolysis to further purify it.
Electrolysis involves immersing copper anodes in an electrolyte containing copper sulphate and sulphuric acid. Pure copper cathodes are then arranged between the anodes and an electric current is passed through the solution. Copper atoms dissolve from the anodes and form copper ions, which then migrate towards the cathodes and are deposited as pure copper atoms.
Sometimes when copper scrap has been tinned or soldered, these elements are retained rather than removing them by refining. This is because bronzes and gun metals often require these elements in their specifications, so it is more cost-effective to retain them. This kind of scrap is instead simply melted, cast into moulds and sent to the foundry.
The purest grade of copper is used for fine and super fine electrical wiring, as it has the best conductive properties. Lower grade copper is used to make everything from heat exchangers to plumbing and roofing materials.
Because recycled copper is worth up to 90% of the value of newly mined copper and requires much less energy to produce, it has been and remains the most sought after non-precious metal for recycling and it will continue to be so into the foreseeable future. [1]
Reasons for recycling copper:
- It’s cheaper to recycle copper, than to diminish it get more.
- Copper is a restricted resource. Till this day only 12% to 13% of all known stocks were diminished.
- It’s energy efficient. For recycling 1 tonne of copper only 15% of the energy which would be used for the dismantling and the production of the same copper are used. Recycling helps to receive the worldwide stock in fossil fuels and to reduce the carbon dioxide issues.
- It’s better for the environment. With the dismantling and the refining of metal, gases & dust are released. while recycling there are practically no issues. This helps the environment.
Why do we need copper?
Copper is a part of very important enzymes. This element is involved in many bodily functions: It works among other things as antioxidants, contributes to the formation of blood, is involed in the production of energy and influences the immune system and inflammations. [4]
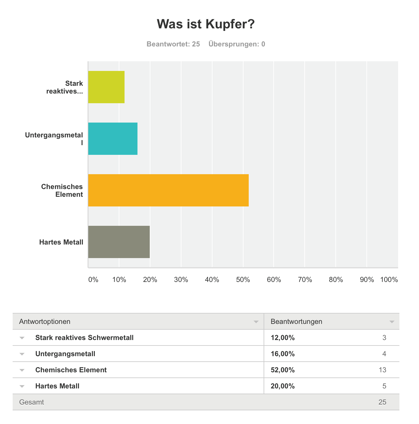
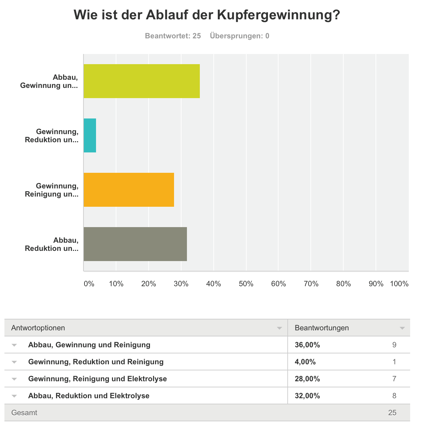
Survey
We made a survey about copper. It was very fascinating to see the results. The answers showed us, that most of the people know what copper is and how copper is produced. [4]
36% of the participants knew, how copper is produced.
52% of the participants knew, what copper is.
Sources:
[1] copperalliance.de
[2] die-handy-connection.jimdo
[3] wikipedia.org
[4] centrosan.com
Abdul, Karen and Alessandrina
Copper comic
by Cécile Kienzi and Kim Löffler
Click on the cartoons to enlarge!
☷ See the project teams here »
☵ Some words about the contributions »
☴ Our sponsors and partners » (the-horse.education)


Dear Copper Team
You did a very good job with your contribution.
There were a lot of interesting facts, like that also the human body has copper in it. Also your video is really good!
Lövlövlöv
Larissa, Valerio and Slavica
Hi Copper Team
Interesting contribution! I did not know much about Copper before I read your post. I think it is a good thing that you did not only mention how to recycle, but also why copper is important to us.
As an improvement I would suggest you add to the sources the website names. In my opinion it would be easier to understand.
Many thanks Fabienne.
Dear copper Team
We are really impressed by your video. It is very creative. Before your contribution, we didn\’t really knew that there are so many things that contain copper. Your contribution is very detailed and well structured. What we miss a little bit is that there is no conclusion at the end.
In conclusion we thank you for this nice contribution. It is very nice!
Love
Your paper Team (Laura, Nicole + Fabienne)
Many thanks! In conclusion, I think copper is really important and we should deal with copper more economically because it\’s a rare source.
Dear Cooper Team
Your post is very interesting! The video is funny and we saw that you put a lot of effort in it, good Job! Well there is one point we are not really happy about, that the extraction part. We would have liked to learn a bit more about that part but the other parts are very good and we learned a lot of new thins, I mean we are all made out of copper?! Amazing!
Thank you and have a nice day! 🙂
Your Tire Team
Lukas, Claudia & Ladina
Thanks for your feedback. The following website will answer your question.
http://www.friedrich-ebert-schule.de/fileadmin/selbstarbeit/metall/textverhuett/kupfergewinnung.pdf
Dear Copper Team
We think that your post is really informative and interesting to read.
You also chose really good pictures for your post which make it even better!
Good job!
Best wishes
Kadri, Dominique and Imre
Many thanks!